Overview
Data literacy training for UW–Madison faculty, staff, and students to find, interpret, and evaluate institutional data.
Audience: UW–Madison faculty, staff, and students
Home Data Literacy & Training
Previous Introduction to the Data Lifecycle
Next Data Literacy Part 2: Using Data Ethically
Learning Objectives
- Gain an understanding of the UW–Madison institutional data landscape
- Identify critical skills needed to evaluate and interpret data
- Understand various access controls and authorization requirements
Introduction
As the caretaker of institutional data, the university has an obligation to protect the integrity and quality of institutional data, privacy of data providers, and security of institutional data while also maximizing its effective and efficient use. This guide brings together best practices, policies, and recommendations for the appropriate use and stewardship of institutional data resources throughout the data lifecycle to help data users find, interpret, evaluate, and effectively use data.
Institutional data landscape
The university maintains hundreds of databases and systems that house institutional data. Any system holding institutional data shall be purposefully planned, inventoried, and implemented to manage institutional data throughout the entire data lifecycle in compliance with all applicable laws; Board of Regents, UW System Administration, and university policies, procedures, and standards; and approved records schedules.
System(s) of record are the single system deemed to be the university’s authoritative instance of a particular data element.
Ancillary systems source their institutional data from system(s) of record. However, to the extent possible, unnecessary duplication or storage of institutional data should be avoided and university standards for integrations shall be followed.
Data warehouses and data lakes combine data from multiple sources for analytics purposes. UW–Madison data warehouses extracts data from enterprise source systems, such as Student Information System (SIS), Budget System, Shared Financial System (SFS), Person Hub and Human Resource System (HRS). Read more about InfoAccess and the migration to Badger Analytics.
Popular UW–Madison Data Systems
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Student Information System (SIS)
The Student Information System (SIS) is an Oracle/PeopleSoft product which serves as the enterprise-wide transactional software that houses student data. It is the infrastructure of UW–Madison’s student administrative services (e.g., admissions, financial aid, student financials, course, and student data). SIS has limited querying and reporting capabilities.
Data Center is a tool within SIS which expands its student and curricular reporting capabilities. Data Center is primarily useful to create lists of students who meet specific user-defined curricular or academic criteria.
Advising Gateway
The Advising Gateway provides a single point of access to student record information for advisors. The Advising Gateway is available through the Advising Tools Catalog.
Degree Audit Reporting System (DARS)
The Degree Audit Reporting System (DARS) is used by advisors and departmental staff to audit the progress of most undergraduate degree programs and certificates to advise their students for registration. Additionally, students can use this tool to see which degree requirements must still be fulfilled.
UW Business Intelligence (UWBI)
UW Business Intelligence (UWBI), also known as Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition (OBIEE), is a business intelligence platform utilized primarily by UW System, but UW–Madison employees can utilize OBIEE to access HR, payroll, and benefits reports.
University of Wisconsin System Data Warehouses
WISDM / WISER: access to data from the Shared Financial System (SFS).
EPM: access to data from the Human Resource System (HRS).
Finding data
Data discovery tools include catalogs (where datasets are described but not stored) and repositories (where data are described and stored) or a combination of multiple sources known as aggregators.
UW–Madison Data Catalogs
- RADAR: The UW–Madison data catalog for institutional data sources, interactive data reports, and data visualizations (e.g., Tableau dashboards).
- Data Digest: Annual overview of trends in the students, faculty and budget of the university provided by DAPIR.
Global data catalogs and repositories
- Worldwide government data: http://data.un.org
- US government data: http://data.gov
- State and city data (search for your local civic data repository)
- Wikidata: https://www.wikidata.org
- Google Dataset Search: https://datasetsearch.research.google.com/
- International index of data repositories: http://re3data.org
- DataCite Commons: https://commons.datacite.org
Understanding and evaluating data fitness for purpose
General things to ask yourself when understanding and evaluating data for use:
- Why was this data collected?
- How was this data collected and managed over its lifecycle?
- Who performed the data collection?
- What quality control measures were in place during data collection?
- What data is included in this sample (e.g., raw or processed? aggregated sample? limited sample?)? Was any data removed and why?
- If data was collected from individuals, who is represented in this sample and who may be missing?
- What documentation and metadata exists to understand the data collection process (e.g., survey instrument used, detailed processing notes, reproducible analysis protocol)?
- Under what conditions may I reuse this data?
Access to UW–Madison institutional data
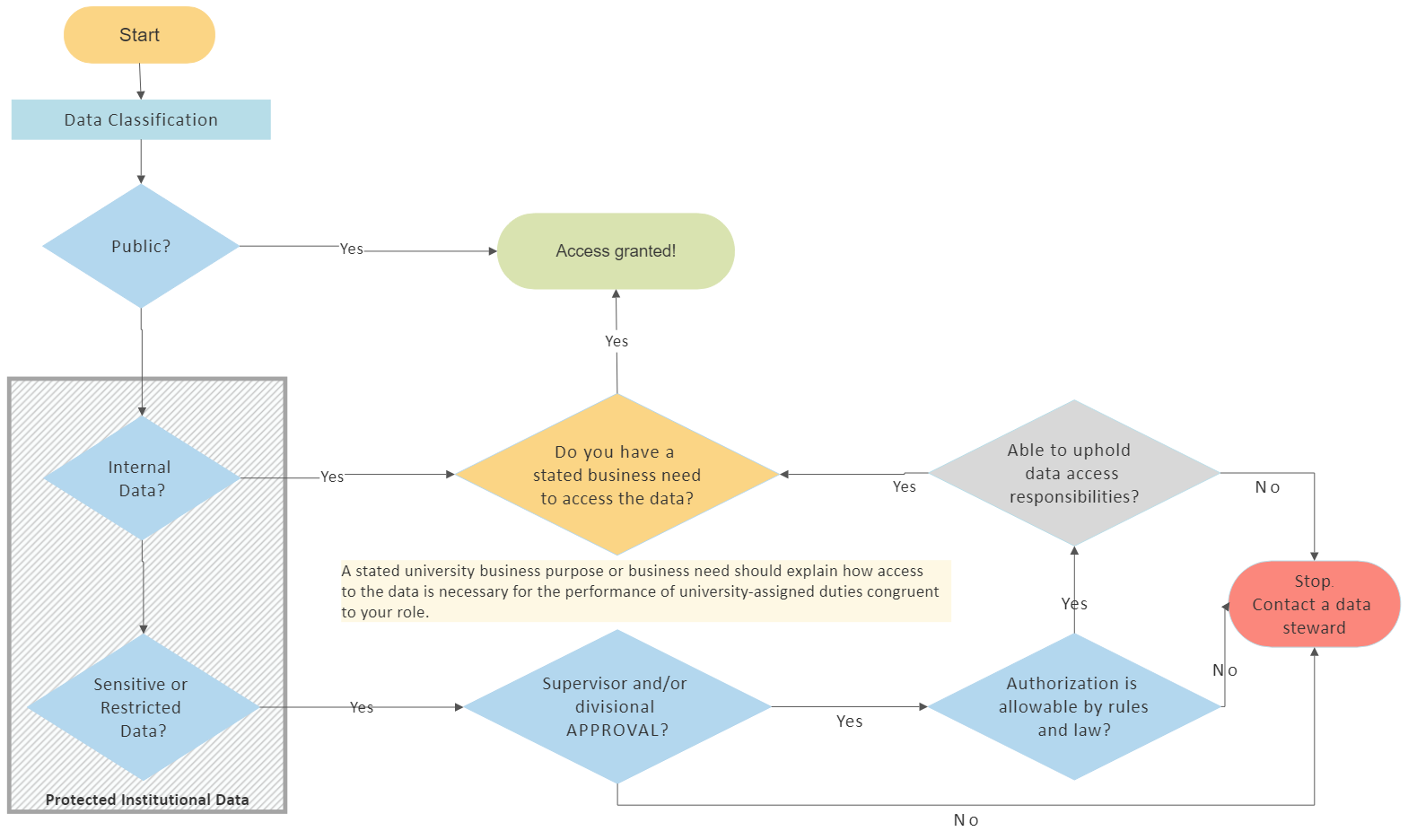
Access to protected institutional data (e.g., data not released publicly) is strictly managed. Access is granted by an appropriate data steward following the process outlined in the UW–Madison Institutional Data Access and Authorization Standard (March 1, 2021).
Tip: Learn more about how to request access to institutional data dashboards and reports.
Based on what criteria? Individuals will be authorized to access protected institutional data based on:
- The security classification of the data
- The stated business purpose of the need or intended use of the data
- Their agreement to any necessary conditions. For example:
- I will access only the information I need to perform my university-assigned responsibilities.
- I will make every reasonable effort to maintain privacy of the data.
- I will not share institutional data with others unless they are explicitly authorized to access it.
- I will not share my account information or password with others.
Acknowledgement of Responsibilities for Sensitive and Restricted Data
Authorization for some institutional data at UW Madison requires acknowledgement and acceptance of certain obligations and responsibilities. As an individual authorized to access sensitive or restricted institutional data, you must take reasonable steps to protect sensitive or restricted institutional data that you may have access to in the course of business and the normal execution of your job.
General Obligations and Responsibilities
Authorization of access to sensitive or restricted institutional data carries with it the following obligations and responsibilities:
- You will access only the information you need to perform your university-assigned responsibilities.
- You will make every reasonable effort to maintain privacy of the data. This includes minimizing exposure of identifiable institutional data.
- You will share sensitive or restricted institutional data only with those who are explicitly authorized to access it under applicable laws, regulations, policies, standards, and procedures.
- You will not share your account information or password with others.
- You will sign out of institutional data systems and applications when not using them.
- You will store under secure conditions all data that you obtain from on-line pages, data warehouse or extracted datasets, including printed data as well as on-line transmissions of data (email, fax). Using and storing Social Security Numbers is strongly discouraged.
- You will encrypt confidential information on my university-owned computer, laptop, mobile device or removable storage device (e.g. thumb drive) whenever possible.
- You will be a responsible user of data, whether it is data relating to your own unit or another unit.
- You will make every reasonable effort to interpret data accurately and in a professional manner.
- You will make every reasonable attempt to maintain the integrity of the data. This includes making only the changes that you are authorized to make and doing so in an appropriate manner.
- You will report any actions which violate confidentiality to your supervisor or the Information Technology Security Officer.
Example Acknowledgement and Agreement:
I understand my obligations with respect to the sensitive or restricted institutional data for which I have been authorized. By signing this form I certify that I have a university business purpose for the sensitive or restricted institutional data for which I am authorized and I agree to abide by Federal and State laws; Board of Regents, UW System Administration, and UW-Madison policies, procedures, and standards; and approved
records schedules that apply to the proper use and protection of the data for which I am authorized.